Ethylene Oxide: The Versatile Industrial Gas with a Wide Range of Applications
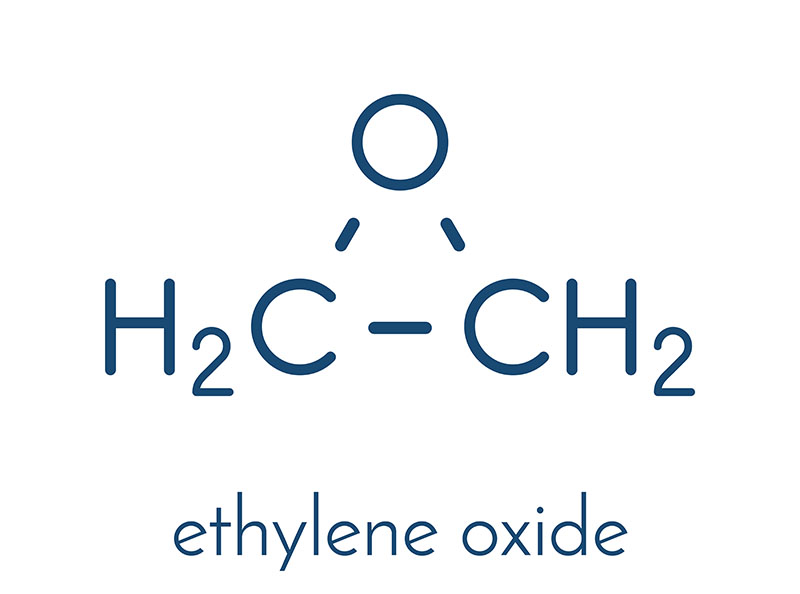
Ethylene oxide, a colorless, flammable gas with a faintly sweet odor, packs a punch despite its seemingly simple molecular structure. This small molecule, composed of two carbon atoms, four hydrogen atoms, and one oxygen atom, plays a significant role in various industrial processes, from sterilizing medical equipment to manufacturing essential chemicals.
Production and Properties:
Ethylene oxide is primarily produced through the direct oxidation of ethylene, using a silver catalyst. This process yields ethylene oxide alongside carbon dioxide and water. The gas is highly reactive and readily undergoes addition reactions with various nucleophiles. This reactivity, coupled with its relatively low toxicity compared to other sterilizing agents like formaldehyde, makes it a valuable tool in various industrial applications.
 |
| Ethylene Oxide: The Versatile Industrial Gas with a Wide Range of Applications |
Sterilization:
One of the most prominent uses of ethylene oxide is in sterilization. Its ability to alkylate DNA and RNA molecules effectively renders microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores, inactive. This makes it ideal for sterilizing medical equipment, pharmaceuticals, and other sensitive products that cannot withstand the high temperatures or harsh chemicals used in other sterilization techniques. The effectiveness of ethylene oxide sterilization is particularly valuable in healthcare settings, where preventing the spread of infections is crucial.
Chemical Synthesis:
Beyond its sterilization prowess, ethylene oxide serves as a key building block in the synthesis of various industrial chemicals. It is a major precursor to:
- Ethylene glycol: This versatile compound finds applications in antifreeze, polyester fibers, and plastic bottles.
- Ethanolamines: These amines are used in a variety of industries, including the manufacture of detergents, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.
- Polyether polyols: These are essential components of polyurethane foams, which are widely used in insulation, furniture, and packaging materials.
- Textile auxiliaries: Ethylene oxide-derived chemicals are used to modify and improve the properties of textiles, such as improving their softness, wrinkle resistance, and flame retardancy.
Fumigation:
Ethylene oxide's antimicrobial properties also extend to its use in fumigation. It is used to control pests and insects in stored grains, spices, and other agricultural products. Additionally, it is sometimes employed to disinfect buildings and equipment contaminated with harmful microorganisms.
Other Applications:
Ethylene oxide's versatility extends beyond the aforementioned uses. It also finds applications in:
- Food preservation: Ethylene oxide can be used to extend the shelf life of certain fruits and vegetables by slowing down their ripening process.
- Cosmetics: Ethylene oxide-derived chemicals are used as thickeners and emulsifiers in various cosmetic products.
- Solvents: Ethylene oxide is used as a solvent in the production of certain polymers and coatings.
- Lubricants: Ethylene oxide-derived chemicals are used as lubricants in various industrial applications.
Environmental and Safety Considerations:
While ethylene oxide offers numerous benefits in industrial applications, it is essential to consider its environmental and safety implications. Ethylene oxide is classified as a potential human carcinogen and can cause irritation to the eyes and respiratory system upon exposure. Additionally, it contributes to the formation of ground-level ozone, a major component of smog.
Regulations and Controls:
Strict regulations govern the production, use, and disposal of ethylene oxide to minimize environmental and health risks. These regulations include:
- Emission limits: Industrial facilities must comply with regulations that limit the amount of ethylene oxide released into the atmosphere.
- Safe handling procedures: Workers who handle ethylene oxide must wear appropriate personal protective equipment and follow safe handling protocols.
- Waste disposal: Proper waste disposal procedures are crucial to prevent ethylene oxide from contaminating the environment.
Future of Ethylene Oxide:
Despite the environmental and safety concerns, ethylene oxide remains a valuable tool in various industrial processes. Research efforts are focused on developing more efficient and safer production methods while minimizing environmental impact. Additionally, exploring alternative sterilization and fumigation techniques with lower environmental and health risks is ongoing.
Conclusion:
Ethylene oxide plays a crucial role in numerous industrial applications, contributing to a range of products and processes we encounter daily. Its versatility and effectiveness are undeniable. However, it is essential to acknowledge its environmental and safety concerns. As we move forward, ensuring the safe and responsible use of ethylene oxide while exploring alternative solutions should be paramount.






