Zero Trust Security: A Paradigm Shift in Cybersecurity
In the realm of cybersecurity, the concept of Zero Trust has emerged as a transformative approach, challenging traditional notions of network security. While traditional security models rely on the implicit trust of users and devices within a defined network perimeter, Zero Trust adopts a "never trust, always verify" philosophy, continuously validating access and privileges throughout the entire network environment.
The Origins of Zero Trust
The term "Zero Trust" was coined by John Kindervag, an analyst at Forrester Research, in 2009. Kindervag recognized the growing sophistication of cyberattacks and the inherent flaws in traditional perimeter-based security models. He proposed Zero Trust as a new paradigm that would address these vulnerabilities by assuming that no user or device should be inherently trusted, regardless of their location or presumed identity.
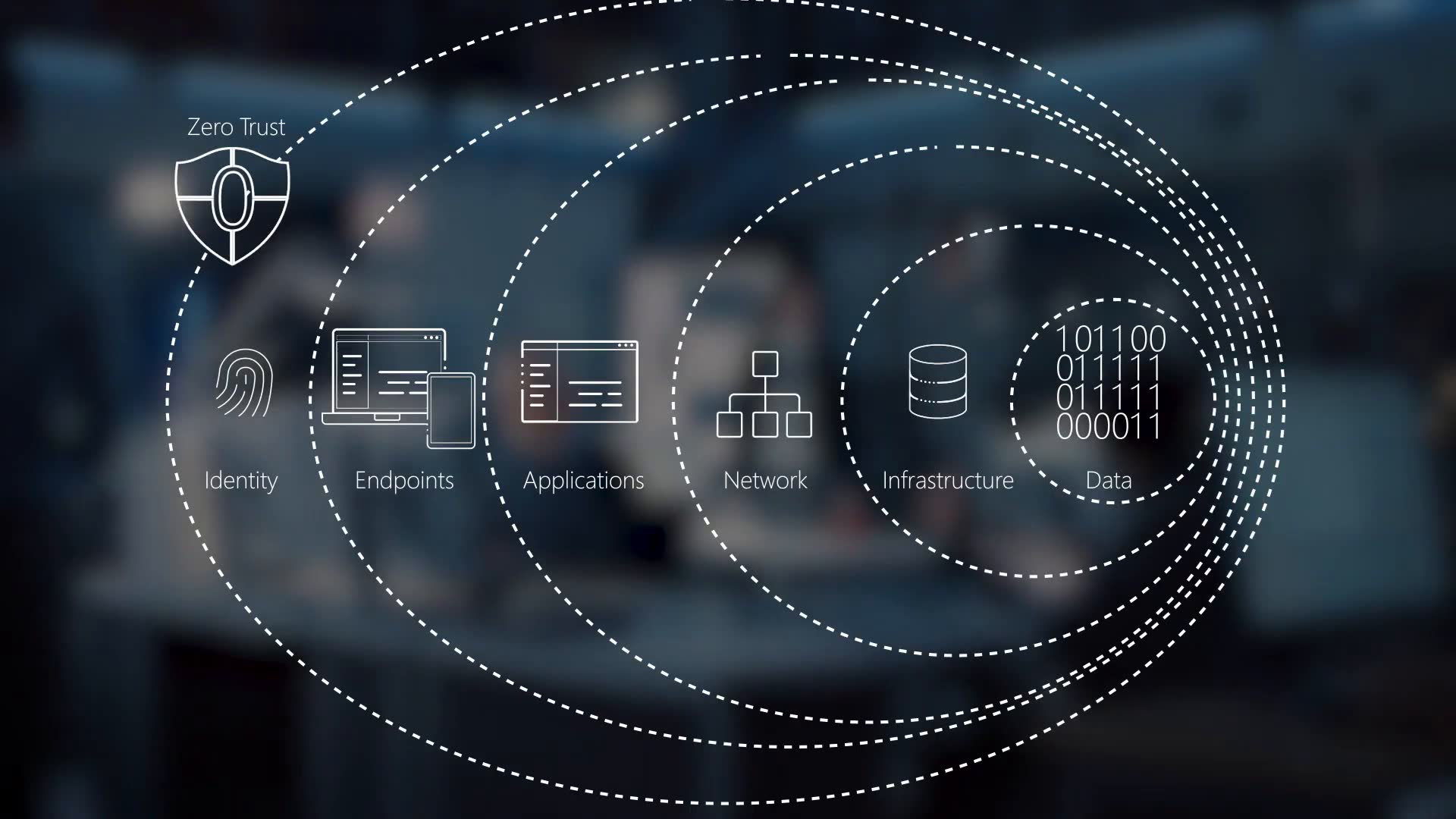 |
| Zero Trust Security: A Paradigm Shift in Cybersecurity |
Zero Trust Principles
The Zero Trust model is founded on several key principles:
Never trust, always verify: Continuously authenticate and authorize all users and devices, including those within the network perimeter.
Least privilege: Grant users and devices the minimum level of access necessary to perform their tasks.
Continuous monitoring and validation: Monitor all network activity and continuously validate access permissions.
Assume breach: Design security systems to assume that a breach has already occurred.
Zero Trust Architecture
A Zero Trust architecture encompasses a set of technologies and practices that implement the Zero Trust principles. These technologies include:
Identity and access management (IAM): IAM solutions manage user identities and access permissions, ensuring that only authorized users can access authorized resources.
Micro-segmentation: Micro-segmentation divides the network into smaller, more manageable segments, limiting the lateral movement of attackers.
Data loss prevention (DLP): DLP solutions prevent sensitive data from being exfiltrated from the network.
Endpoint security: Endpoint security solutions protect endpoints, such as laptops, desktops, and mobile devices, from malware and other threats.
Benefits of Zero Trust
Zero Trust offers several benefits over traditional security models, including:
Reduced risk of breaches: Zero Trust makes it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive resources.
Improved compliance: Zero Trust can help organizations meet compliance requirements related to data security and privacy.
Enhanced agility: Zero Trust enables organizations to adapt to changing security threats and technologies more quickly.
Challenges
of Implementing Zero Trust
Implementing Zero Trust can be a complex and time-consuming undertaking. Some of the challenges include:
Changing organizational culture: Zero Trust requires a shift in organizational culture, from trusting users and devices to continuously verifying their identities and access permissions.
Integration with existing systems: Integrating Zero Trust technologies with existing IT systems can be challenging.
Cost: Implementing Zero Trust can be more expensive than traditional security models.
Zero Trust security represents a paradigm shift in cybersecurity, moving away from the limitations of traditional perimeter-based models and embracing a continuous verification and access control approach. While challenges exist in implementing Zero Trust, the benefits in terms of enhanced security and reduced risk make it a worthwhile investment for organizations of all sizes. As cyberattacks continue to evolve, Zero Trust is likely to become the standard for cybersecurity in the years to come.






